Proven strategies, common pitfalls, and the roadmap that successful pharmaceutical companies follow
The pharmaceutical executive's frustration was palpable. "We've been working on this traceability project for eighteen months," she said. "We're millions over budget, six months behind schedule, and we still can't track a single product end-to-end. Where did we go wrong?"
This conversation, unfortunately, represents the reality many pharmaceutical companies face during complex technology implementations. While specific failure rates for traceability projects aren't definitively documented, industry experience shows that successful implementations require significantly more organizational transformation focus than technology focus. Companies that treat traceability as purely a technology project consistently struggle with adoption, timeline delays, and suboptimal results. Yet the 30% that succeed don't just meet compliance requirements—they transform their operations and create lasting competitive advantages.
After implementing complete traceability solutions across numerous multinational pharmaceutical companies, we've identified the critical factors that separate successful implementations from expensive failures. The difference isn't in the technology—it's in the approach, the planning, and the understanding that traceability implementation is fundamentally an organizational transformation, not just a technology deployment.
This guide provides pharmaceutical executives with the proven strategies, practical frameworks, and hard-learned lessons that ensure traceability implementations succeed on time, on budget, and with transformational results.
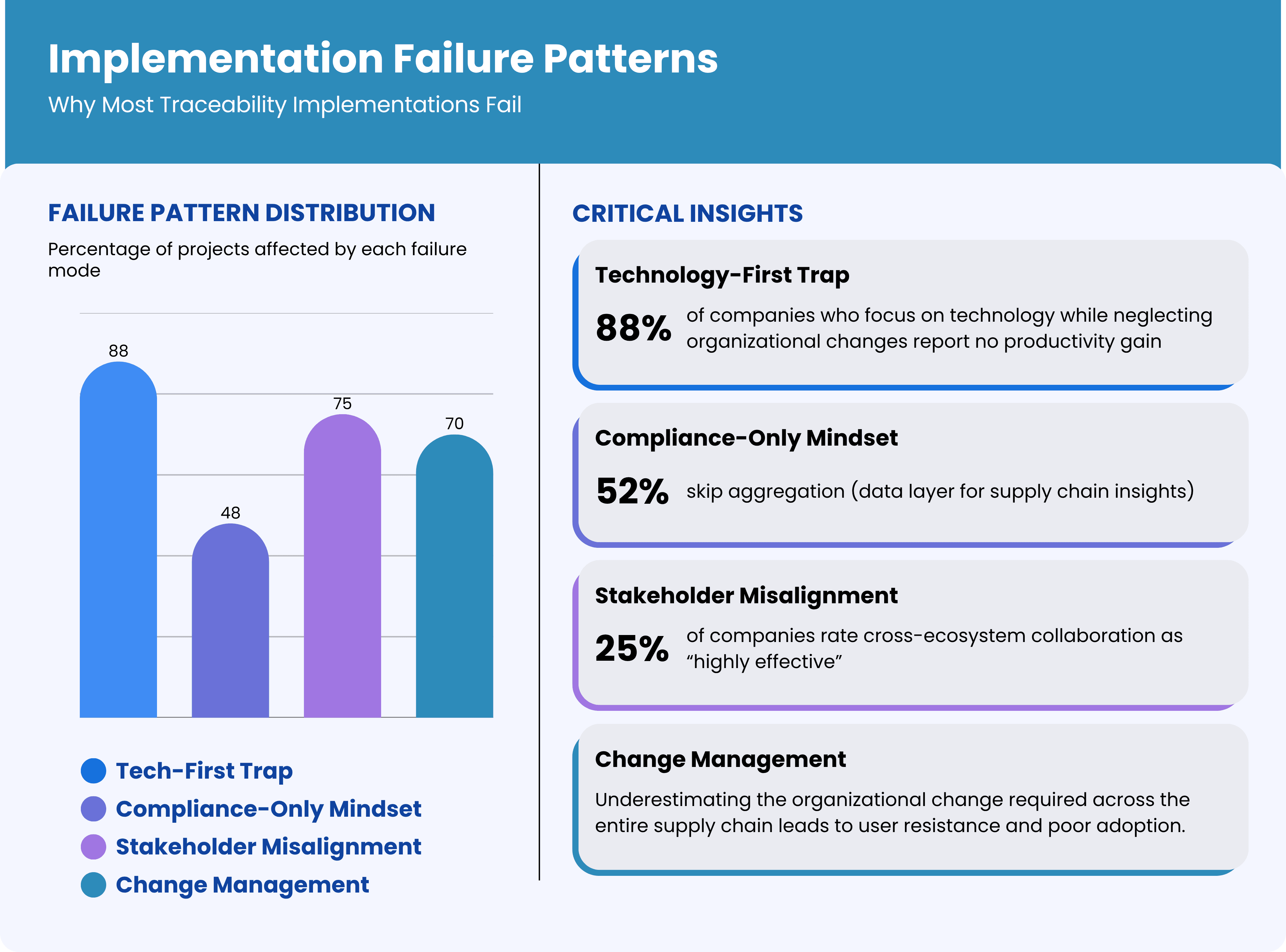
Before diving into success strategies, it's crucial to understand why so many traceability projects stumble. Our analysis of failed implementations reveals consistent patterns:
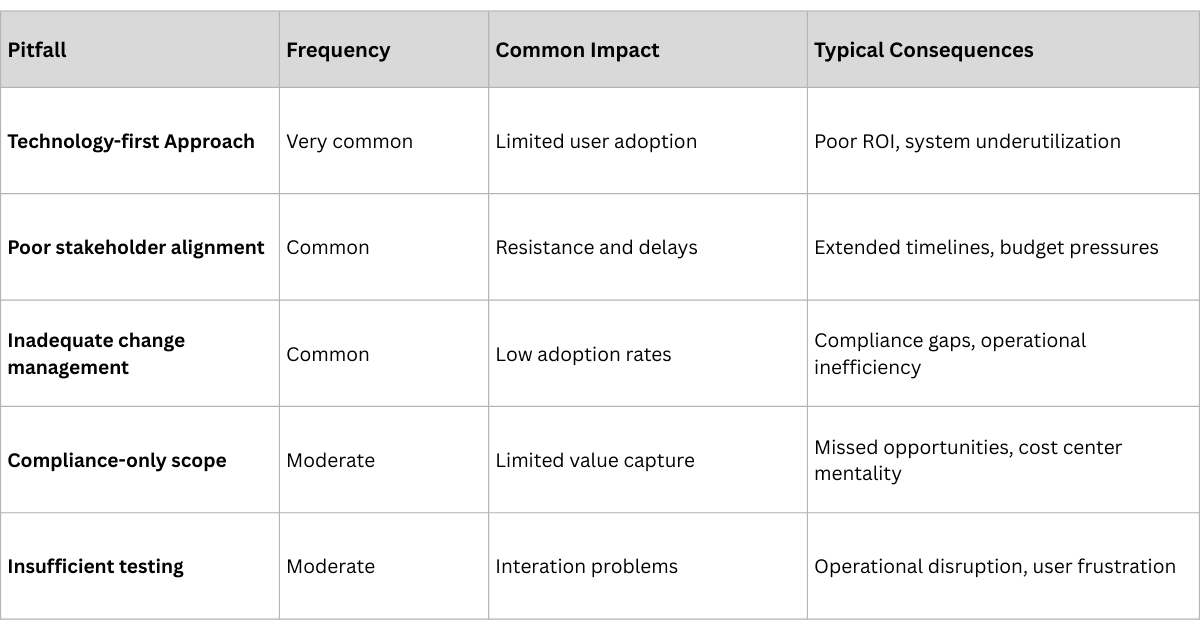
1. The Technology-First Trap
The most common failure mode is treating traceability as a pure technology implementation. Companies focus on selecting software platforms, installing hardware, and integrating systems while neglecting the organizational and process changes required for success. Technology is the enabler, not the solution. In one 11-site Irish study, serialization capital costs averaged €600,000 per line—four times regulatory estimates—yet 88% of sites reported no net productivity gain.
2. Stakeholder Misalignment
Pharmaceutical traceability involves multiple stakeholders—manufacturers, distributors, pharmacies, regulators—each with different priorities, systems, and incentives. Projects that don't address stakeholder alignment from day one inevitably face resistance, adoption problems, and integration challenges. End-to-end pharmaceutical traceability touches manufacturers, CMOs, 3PLs, wholesalers, hospitals, pharmacies, and regulators. Bain’s Global State of Traceability survey found only 25% of companies rate their cross-ecosystem collaboration as “highly effective”.
3. Compliance-Only Mindset
Companies that implement traceability solely for regulatory compliance build systems that meet minimum requirements but miss opportunities for operational improvement and competitive advantage. These implementations often become cost centers rather than value creators. A 2021 PMMI survey notes that 52% of pharma plants implementing US DSCSA standards skipped aggregation—the data layer required for actionable supply-chain insights—because “it wasn’t mandated”.
4. Underestimating Change Management
Traceability implementation requires significant changes to established workflows, processes, and behaviors across the entire supply chain. Companies that underestimate the change management component face user resistance, poor adoption, and suboptimal results.
Successful traceability implementations follow a structured approach that addresses technology, people, processes, and organizational alignment simultaneously. Our framework consists of five phases, each with specific objectives, deliverables, and success criteria.
The foundation phase establishes the strategic context, defines success criteria, and aligns stakeholders around common objectives.
- Current State Assessment: Comprehensive evaluation of existing tracking capabilities, system integrations, and process maturity
- Stakeholder Mapping: Identification of all internal and external stakeholders, their requirements, and success criteria
- Value Case Development: Quantification of business benefits beyond compliance, including operational improvements and competitive advantages
- Success Metrics Definition: Clear, measurable KPIs that define project success and ongoing value realization
- Implementation scope and phasing strategy
- Technology platform selection criteria
- Organizational structure and governance model
- Budget allocation and resource commitment
- Complete stakeholder buy-in on project scope and objectives
- Quantified business case with clear ROI projections
- Defined success metrics and measurement framework
- Approved budget and resource allocation
- Project governance structure established
Success Indicator: All key stakeholders can articulate the project's strategic value beyond compliance
The architecture phase focuses on technology platform selection, system design, and integration planning.
- Cloud-First Approach: Leverages scalability, security, and cost efficiency of modern cloud platforms
- API-Enabled Integration: Ensures seamless connectivity with existing and future systems
- Data Standardization: Implements GS1 standards for interoperability and compliance
- Security by Design: Embeds robust security controls throughout the platform architecture
Successful implementations require careful integration with existing enterprise systems:
Traceability Platform Integration Map:
ERP Systems → Product Master Data, Inventory Management
MES Systems → Production Data, Batch Records
CRM Systems → Customer Information, Sales Data
WMS Systems → Warehouse Operations, Shipping
Analytics → Business Intelligence, Reporting
- Detailed technical architecture documentation
- Selected technology platform and vendor contracts
- Integration specifications and development plans
- Security and compliance framework
- Proof-of-concept validation results
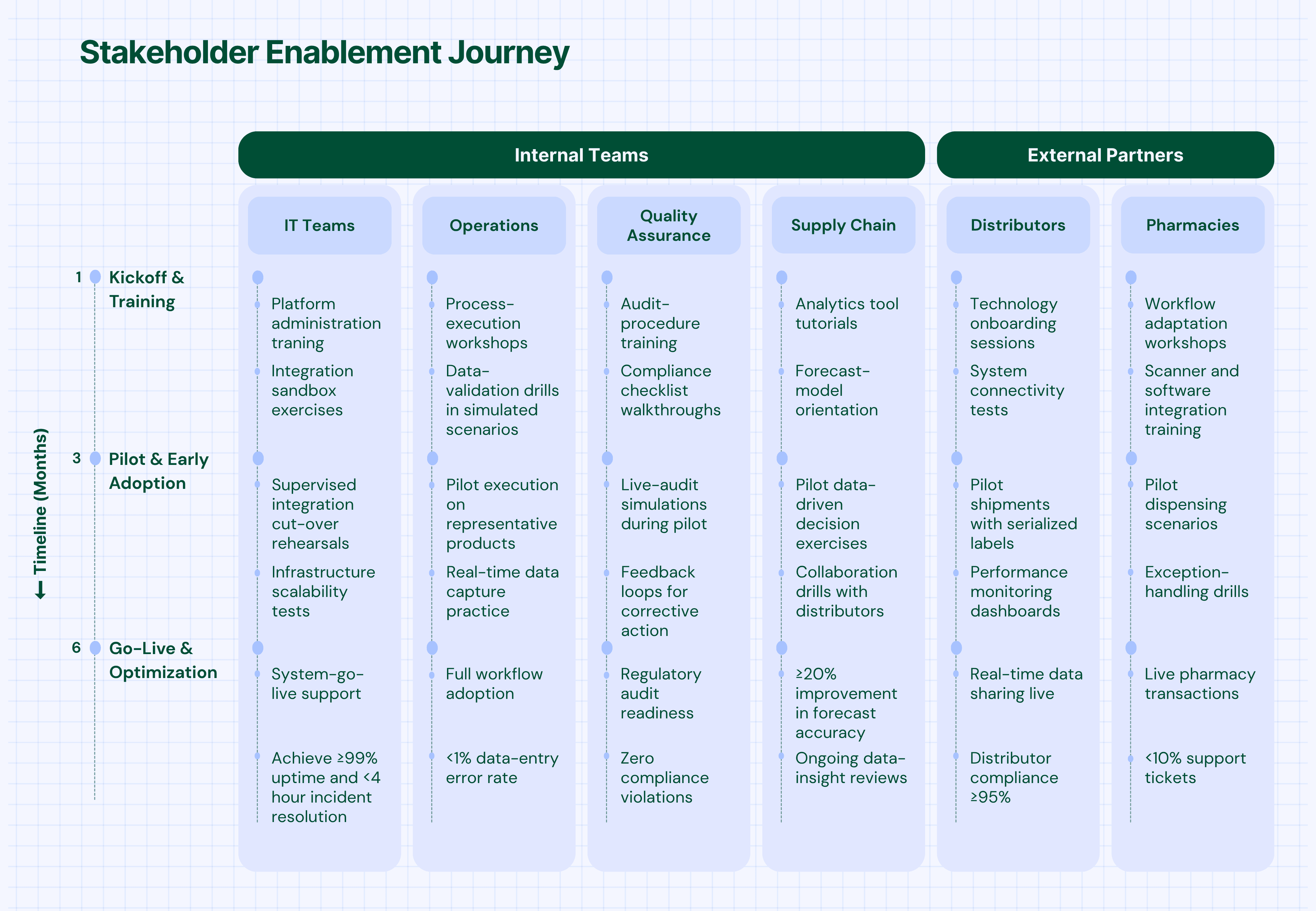
The enablement phase focuses on preparing all stakeholders—internal teams and external partners—for successful adoption.
- Distributor Enablement: Technology deployment, process training, performance monitoring
- Pharmacy Integration: System connectivity, workflow adaptation, support provision
- Logistics Coordination: Real-time data sharing, exception handling, performance tracking
Successful adoption requires comprehensive change management addressing both technical and cultural aspects:
- Executive Sponsorship: Visible leadership commitment and strategic messaging
- Regular Updates: Bi-weekly progress communications and success story sharing
- Feedback Mechanisms: Structured channels for user input and continuous improvement
- Recognition Programs: Celebrating early adopters and implementation milestones
- Role-Specific Training: Customized programs for different user types and responsibilities
- Hands-On Practice: Simulated environments for safe learning and skill development
- Ongoing Support: Help desk, documentation, and peer support networks
- Continuous Learning: Regular updates on new features and best practices
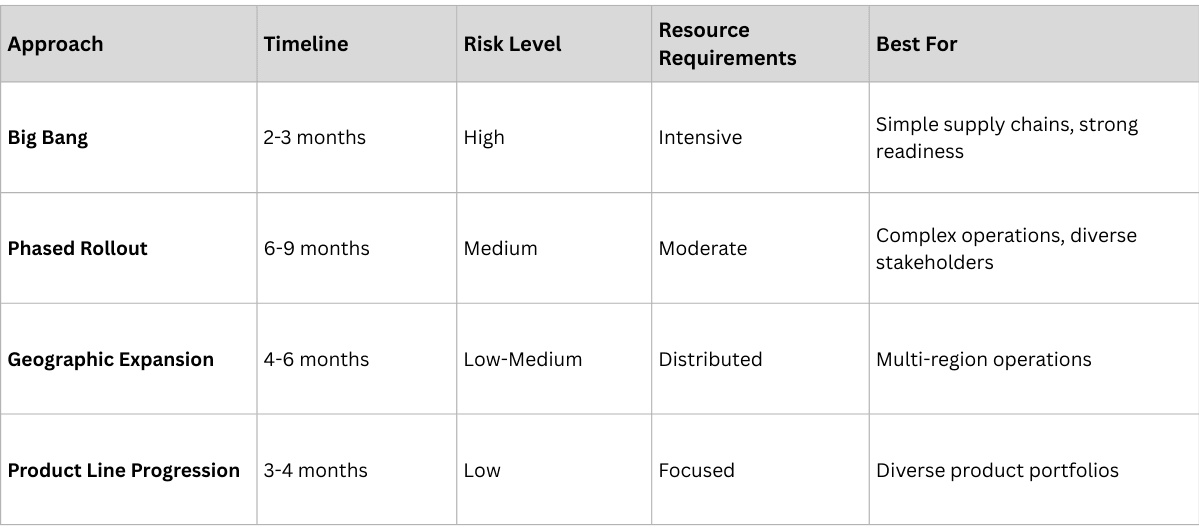
The pilot phase validates the solution with a limited scope before full-scale deployment.
- Representative Products: Include high-value, high-volume, and complex products
- Diverse Geography: Test in different regulatory environments and market conditions
- Varied Stakeholders: Include different distributor types, pharmacy formats, and customer segments
- Manageable Scale: Large enough to validate capabilities, small enough to manage risks
Pilot Success Framework
- Parallel Operations: Run new and old systems simultaneously during transitionm
- Rollback Procedures: Detailed plans for reverting to previous state if needed
- Escalation Protocols: Clear procedures for rapid issue resolution
- Stakeholder Communication: Proactive updates on pilot progress and lessons learned
The pilot phase should include structured evaluation and optimization cycles:
- Initial user feedback collection
- Technical performance validation
- Quick fixes and configuration adjustments
- Comprehensive performance analysis
- User adoption assessment
- Process refinement implementation
- Advanced feature activation
- Integration enhancement
- Scaling preparation
The deployment phase scales the solution across the entire organization and supply chain.
- Final system testing and performance validation
- Stakeholder readiness confirmation and sign-off
- Support team preparation and resource allocation
- Communication campaign launch and awareness building
- Coordinated go-live activities across all stakeholders
- Real-time monitoring and issue response
- User support and immediate problem resolution
- Performance tracking and optimization
Post-Deployment Stabilization:
- 30-day performance monitoring and optimization
- User feedback collection and system refinement
- Advanced feature activation and capability expansion
- Success measurement and ROI validation
Our experience across multiple implementations has identified several factors that consistently determine success:
- Successful implementations require visible, consistent executive sponsorship that:
- Communicates strategic importance and expected benefits
- Resolves cross-functional conflicts and resource constraints
- Maintains momentum through inevitable challenges and setbacks
- Celebrates milestones and recognizes contributor efforts
- Steering Committee: Senior executives providing strategic oversight and decision-making authority
- Project Management Office: Day-to-day coordination, timeline management, and resource allocation
- Technical Working Groups: Subject matter experts addressing specific implementation challenges
- User Advisory Groups: Representative stakeholders providing feedback and guidance
Modern traceability implementations should leverage cloud platforms for:
- Scalability: Ability to handle varying transaction volumes and geographic expansion
- Reliability: Enterprise-grade uptime and disaster recovery capabilities
- Security: Advanced security controls and compliance certifications
- Cost Efficiency: Reduced infrastructure investment and maintenance overhead
Ensure full compliance with relevant GS1 standards:
- GTIN (Global Trade Item Number): Unique product identification
- SSCC (Serial Shipping Container Code): Logistics unit identification
- GLN (Global Location Number): Location and entity identification
- EPCIS (Electronic Product Code Information Services): Event data sharing
The platform must integrate seamlessly with existing systems:
- Real-Time Data Exchange: Immediate synchronization with ERP, MES, and CRM systems
- Standardized APIs: Enable future integrations and ecosystem expansion
- Data Quality Controls: Automated validation and error correction capabilities
- Audit Trail Maintenance: Complete traceability of all system interactions
- Data Standards: Consistent formats, definitions, and quality criteria
- Data Ownership: Clear accountability for data accuracy and maintenance
- Data Security: Access controls, encryption, and privacy protection
- Data Lifecycle: Retention policies, archival procedures, and deletion protocols
- Automated Validation: Real-time data quality checks and error flagging
- Exception Handling: Procedures for managing data discrepancies and corrections
- Performance Monitoring: Continuous tracking of data quality metrics
- Continuous Improvement: Regular review and enhancement of data processes
Understanding the true cost of traceability implementation is crucial for realistic planning and stakeholder expectations.
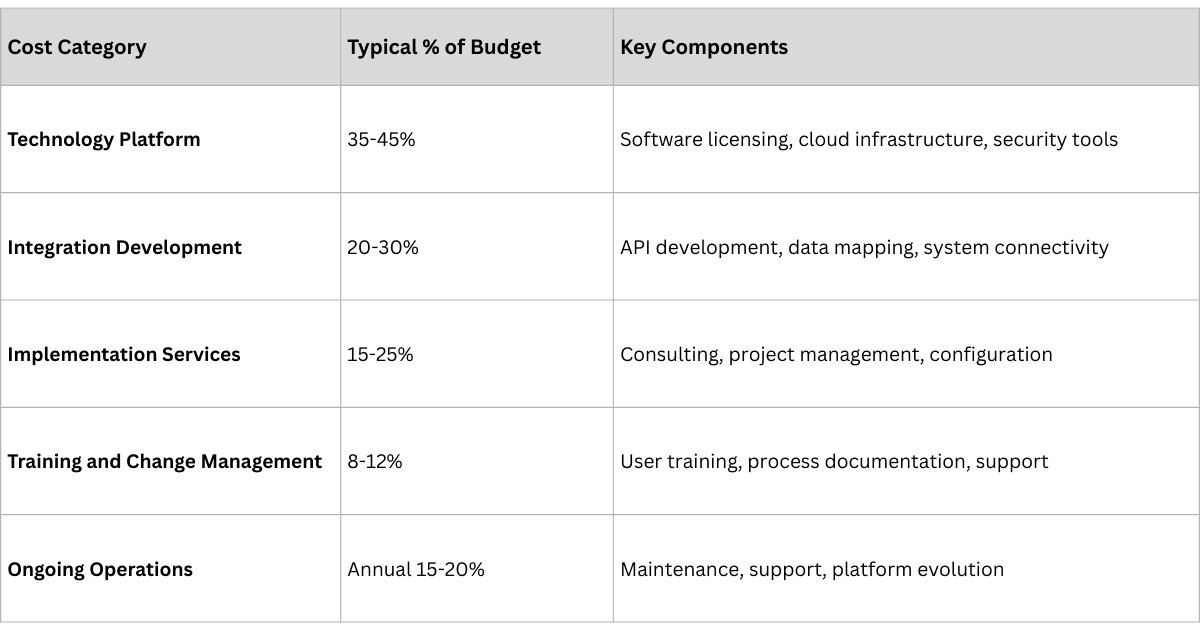
- Total Implementation Cost: $500K - $2M
- Timeline: 6-12 months
- Focus: Compliance achievement with operational efficiency gains
- Total Implementation Cost: $2M - $8M
- Timeline: 12-18 months
- Focus: Advanced analytics and competitive advantage creation
- Total Implementation Cost: $8M - $25M
- Timeline: 18-24 months
- Focus: Global platform with regional customization and innovation
- Regulatory compliance achievement
- Reduced manual processes and associated errors
- Improved audit readiness and inspection outcomes
- 15-25% improvement in inventory management
- 10-20% reduction in product recalls and investigations
- 20-30% faster regulatory reporting and compliance activities
- 25-40% improvement in demand forecasting accuracy
- 10-15% reduction in working capital requirements
- New revenue opportunities through data-driven services
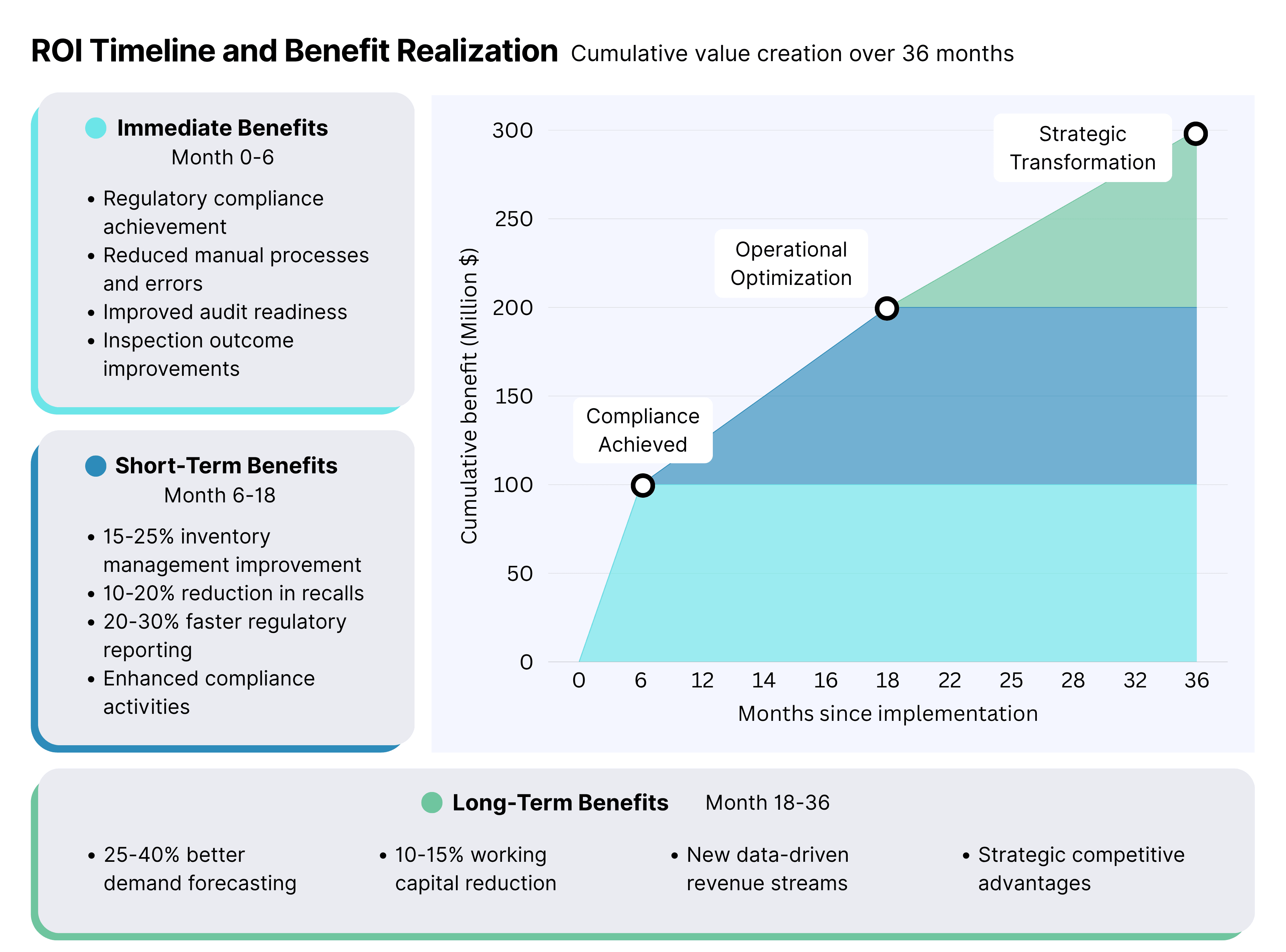
Even well-planned implementations face predictable challenges. Understanding these in advance enables proactive mitigation strategies.
Problem: Inconsistent data formats, incomplete information, and quality issues across different systems and stakeholders.
- Data Mapping and Cleansing: Comprehensive assessment and standardization of existing data
- Validation Rules: Automated checks for completeness, accuracy, and format compliance
- Training Programs: User education on data entry standards and quality requirements
- Continuous Monitoring: Ongoing performance tracking and quality improvement processes
Problem: Users resistant to change, inadequate training, and poor adoption of new processes.
- Early Engagement: Involve stakeholders in requirements gathering and solution design
- Value Communication: Clear articulation of benefits and impact on daily work
- Comprehensive Training: Role-specific programs with hands-on practice and ongoing support
- Incentive Alignment: Recognition programs and performance metrics that encourage adoption
Problem: Difficulty connecting with legacy systems, data format incompatibilities, and performance issues.
- Phased Integration: Gradual connection of systems with thorough testing at each stage
- Middleware Solutions: Use of integration platforms to manage complexity and reduce risk
- API Strategy: Standardized interfaces for future connectivity and ecosystem expansion
- Performance Optimization: Load testing and optimization to ensure acceptable response times
Problem: Varying requirements across different markets, evolving regulations, and audit readiness.
- Regulatory Expertise: Engagement of specialists familiar with relevant requirements
- Compliance Mapping: Detailed analysis of requirements and solution capabilities
- Audit Preparation: Structured processes for maintaining compliance evidence
- Regulatory Monitoring: Ongoing tracking of requirement changes and impact assessment
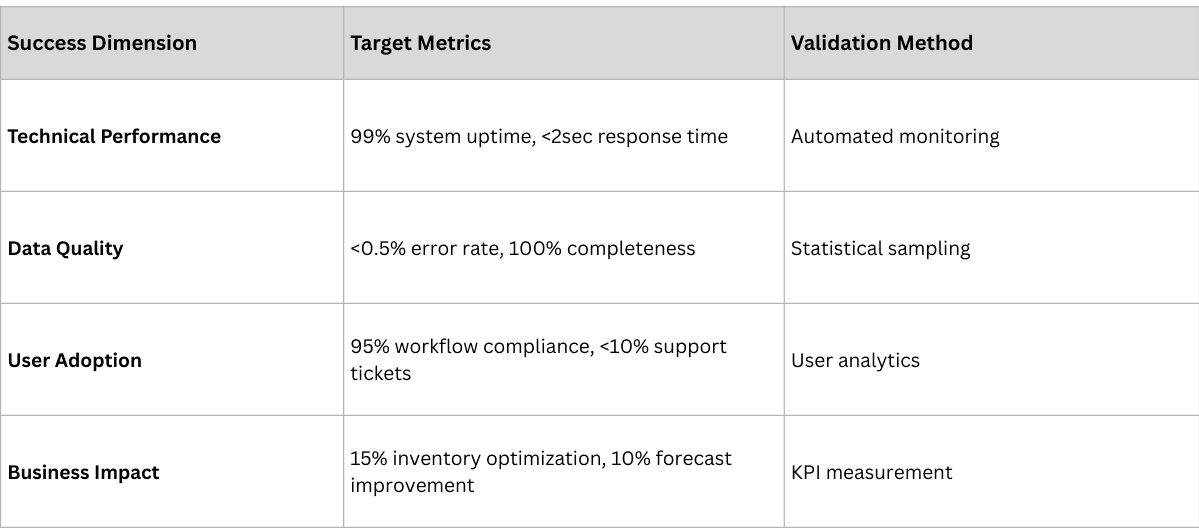
Successful implementations require comprehensive measurement frameworks that track both project execution and business impact.
Project Execution Metrics
- Data quality improvement (target: >98% accuracy)
- Process efficiency gains (target: 20-30% reduction in manual effort)
- Error reduction (target: 50-75% fewer compliance violations)
- Audit readiness (target: <48 hours for regulatory responses)
- Working capital optimization (target: 10-20% reduction)
- Inventory management improvement (target: 15-25% better turns)
- Cost reduction (target: 5-10% operational cost savings)
- Revenue enhancement (target: new service opportunities)
- Market intelligence quality (target: real-time visibility)
- Decision-making speed (target: 50% faster strategic responses)
- Competitive advantage creation (target: measurable market differentiation)
- Innovation enablement (target: new business model opportunities)
Successful traceability implementations must be designed for evolution and adaptation as technology, regulations, and business requirements change.
- Artificial Intelligence: Predictive analytics, anomaly detection, automated decision-making
- Blockchain: Enhanced trust, immutable audit trails, smart contract automation
- IoT Integration: Real-time environmental monitoring, automated data capture
- Advanced Analytics: Machine learning, pattern recognition, optimization algorithms
- Modular Architecture: Enable incremental capability addition without system disruption
- API-First Design: Support future integrations and ecosystem expansion
- Cloud-Native Approach: Leverage continuous platform improvements and scaling
- Standards Compliance: Ensure compatibility with evolving industry standards
- Platform flexibility to accommodate different regulatory requirements
- Multi-language and multi-currency support capabilities
- Local compliance management and reporting features
- Regional customization without core system modification
- Monitoring systems for tracking regulatory changes
- Impact assessment processes for requirement modifications
- Agile modification capabilities for rapid compliance adaptation
- Stakeholder communication systems for change management
Implementing complete pharmaceutical traceability is neither simple nor straightforward, but it is absolutely achievable with the right approach, preparation, and execution. The companies that succeed follow proven frameworks, learn from others' experiences, and treat implementation as organizational transformation rather than technology deployment.
- Strategic Clarity: Define success beyond compliance and align stakeholders around common objectives
- Comprehensive Planning: Address technology, people, processes, and organizational change simultaneously
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involve all participants in design, implementation, and optimization
- Phased Execution: Validate approaches through pilots before full-scale deployment
- Continuous Improvement: Monitor performance and optimize operations based on results
The pharmaceutical industry stands at a critical juncture where traceability implementation is shifting from regulatory requirement to competitive necessity. Companies that implement strategically, execute professionally, and optimize continuously will create lasting advantages that extend far beyond compliance.
The framework, strategies, and lessons shared in this guide represent collective learning from multiple successful implementations. While every implementation has unique characteristics, the fundamental principles of success remain consistent: clear strategy, comprehensive planning, stakeholder alignment, and disciplined execution.
The investment in complete traceability implementation is significant, but the benefits—regulatory compliance, operational excellence, and competitive advantage—make it one of the most important strategic initiatives pharmaceutical companies can undertake today.
Next Week: How Traceability Transforms Pharma Business Models - Discover the strategic opportunities that complete traceability unlocks and why leading companies are treating it as a competitive advantage, not just compliance.
About This Series
This implementation guide draws from real-world experience deploying traceability solutions across pharmaceutical companies ranging from mid-sized enterprises to global multinationals. The frameworks and strategies presented have been validated through successful implementations serving millions of patients and processing billions of pharmaceutical transactions.
Previous in This Series:
- Blog 1: Understanding Pharmaceutical Traceability: A Global Landscape and Strategic Overview
Upcoming:
- Blog 3: How Traceability Transforms Pharma Business Models
- White Paper: Beyond Track and Trace - Strategic Business Model Transformation
For specific questions about traceability requirements in your market or to discuss implementation strategies, feel free to reach out to our team at connect@zelthy.com.
- R.G. Mukunda, N. Vishal Gupta. “Pharma Serialization: Implementation and Challenges.” International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences Review and Research, 2015.
- McKinsey & Company. "Digital transformation: Health systems’ investment priorities." Healthcare Industry Report, 2024.
- McKinsey & Company. “Rewired pharma companies will win in the digital age.” Healthcare Industry Report, 2023.
- GS1 US. “Applying GS1 System of Standards for DSCSA and Serialized Interoperable Traceability | Implementation Guideline.” 2022.
- GS1 US. “Implementation Guideline: Applying GS1 Standards for DSCSA and Traceability.” 2016.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. "FDA’s Implementation of Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) Requirements.” 2024.
- The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. "Falsified Medicines Directive." 2011.
- European Commission. “Implementation measures by the commission in context of the falsified medicines directive.”
- GS1 Healthcare. "Healthcare Supply Chain Traceability.” Industry Report.
- Accenture. "Achieving high performance in pharmaceuticals through supply chain analytics."
- Deloitte Insights. Deloitte Centre for Health solutions. "Intelligent drug supply chain: Creating value from AI." 2024.
- Deloitte Insights. Deloitte Centre for Health Solutions. “Pharma’s supply chain workforce.” 2024.
- Vergara, I. T. & McKinnell, D. “Optimising pharmaceutical supply chain digitalisation through serialisation and traceability: A perspective beyond compliance.” Deloitte Blogs, 2023.
- TraceLink. “Global Drug Supply, Safety and Traceability Report.” Industry Report, 2025.
- ISPE (International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering). "Good Practice Guide: Digital Validation." Technical Guidelines, 2025.
- ISPE (International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering). "GAMP 5: A Risk-Based Approach to Compliant GxP Computerized Systems." 2022.
- Alphena Pharma Solutions. “Track and Trace: A Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing an Effective Program.”
- Boston Consulting Group. "Building the Supply Chain of the Future." Strategy Report, 2023.
- O' Mahony, D., Lynch, A., & McDermott, O. (2024). The Impact of Serialisation on Operational Efficiency and Productivity in Irish Pharmaceutical Sites. Therapeutic innovation & regulatory science, 58(5), 883–896. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43441-024-00662-1
- Hernan Saenz, Joshua Hinkel, and Tessa Bysong. “Traceability: The Next Supply Chain Revolution.” Bain & Company. 2021.
- “Serialization will impact all drug manufacturing.” Healthcare Packaging, 2017.











