Why leading pharmaceutical companies are treating traceability as a strategic platform, not just a regulatory requirement
The pharmaceutical executive leaned forward, a mix of excitement and disbelief in her voice. "Six months ago, we implemented traceability for DSCSA compliance," she said. "Today, we're orchestrating insight-enabled programs across the supply chain, compliance, and patient support, our demand forecasting accuracy has improved by 35%, and we've identified $4.2 million in supply chain optimization opportunities. Traceability wasn't supposed to do all that."
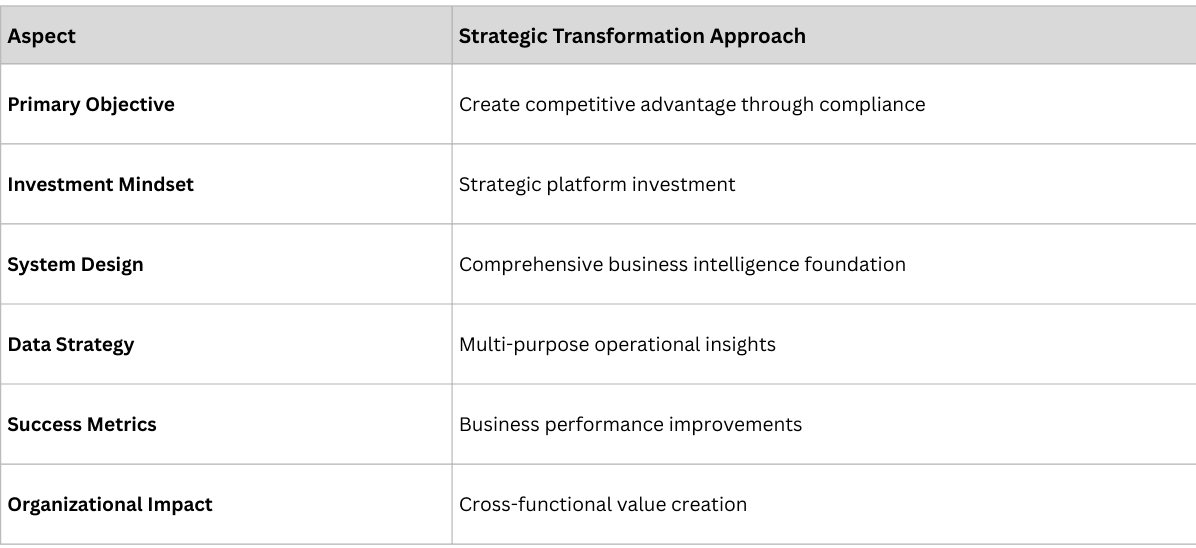
This transformation story, repeated across pharmaceutical companies worldwide, reveals a fundamental shift happening in the industry. While most companies approach traceability as a compliance checkbox, a growing number of market leaders are discovering that complete traceability is actually a business model transformation platform—one that unlocks competitive advantages that extend far beyond regulatory requirements.
After implementing traceability solutions across numerous multinational pharmaceutical companies, we've witnessed this evolution firsthand. Companies that embrace traceability strategically don't just achieve compliance—they reshape their operations, optimize revenue and margins through better allocation, adherence, and waste reduction, and build competitive moats that competitors struggle to replicate.
This shift represents one of the most significant opportunities in pharmaceutical business model innovation today. The question is: will your company lead this transformation or follow it?
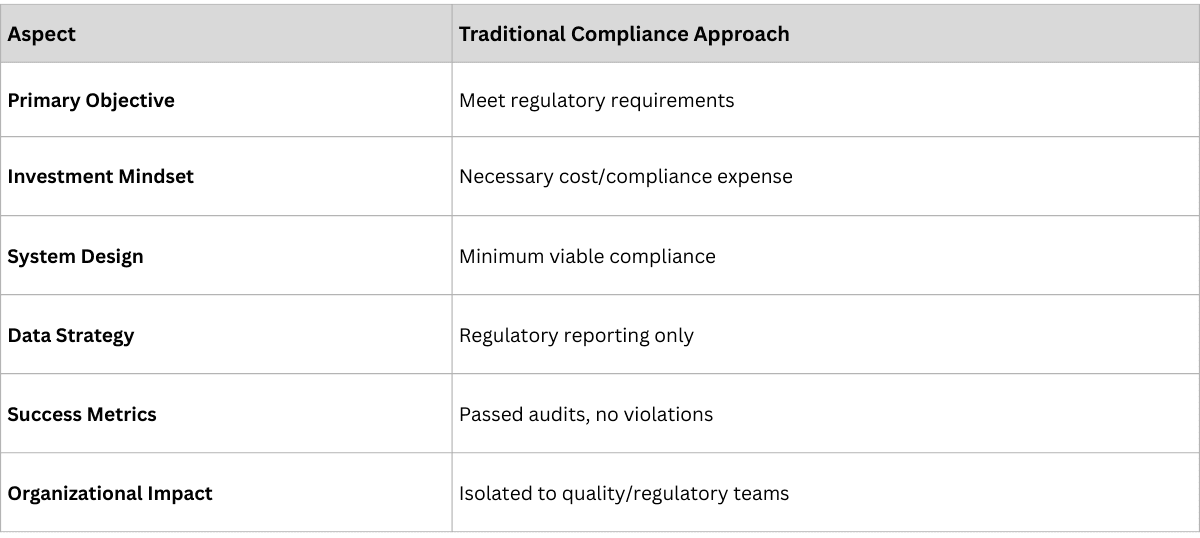
For most pharmaceutical executives, traceability begins as a regulatory burden. The Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA), the Falsified Medicines Directive (FMD), and similar regulations worldwide demand serialization, verification, and tracking capabilities. Companies invest millions to achieve compliance, often viewing these systems as necessary costs rather than value creators.
But something remarkable happens when companies build robust traceability infrastructure: they suddenly gain access to what is essentially real-time secondary and tertiary sales data — visibility into how products move through distributors, pharmacies, and to patients. What begins as a compliance system becomes a continuous source of market intelligence.
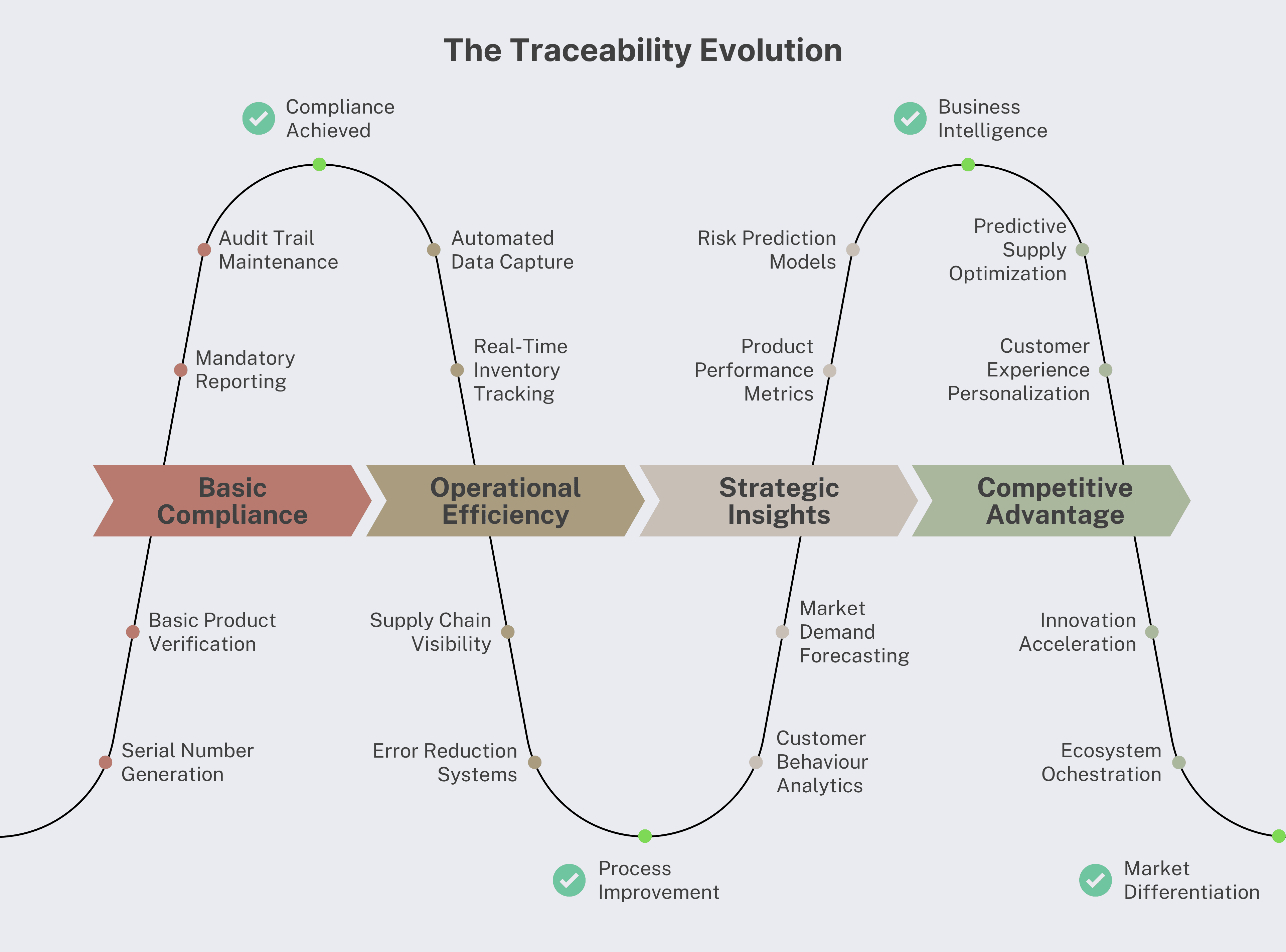
Our experience across multiple implementations reveals four distinct ways complete traceability transforms pharmaceutical business models. Each represents a paradigm shift that creates lasting competitive advantages.
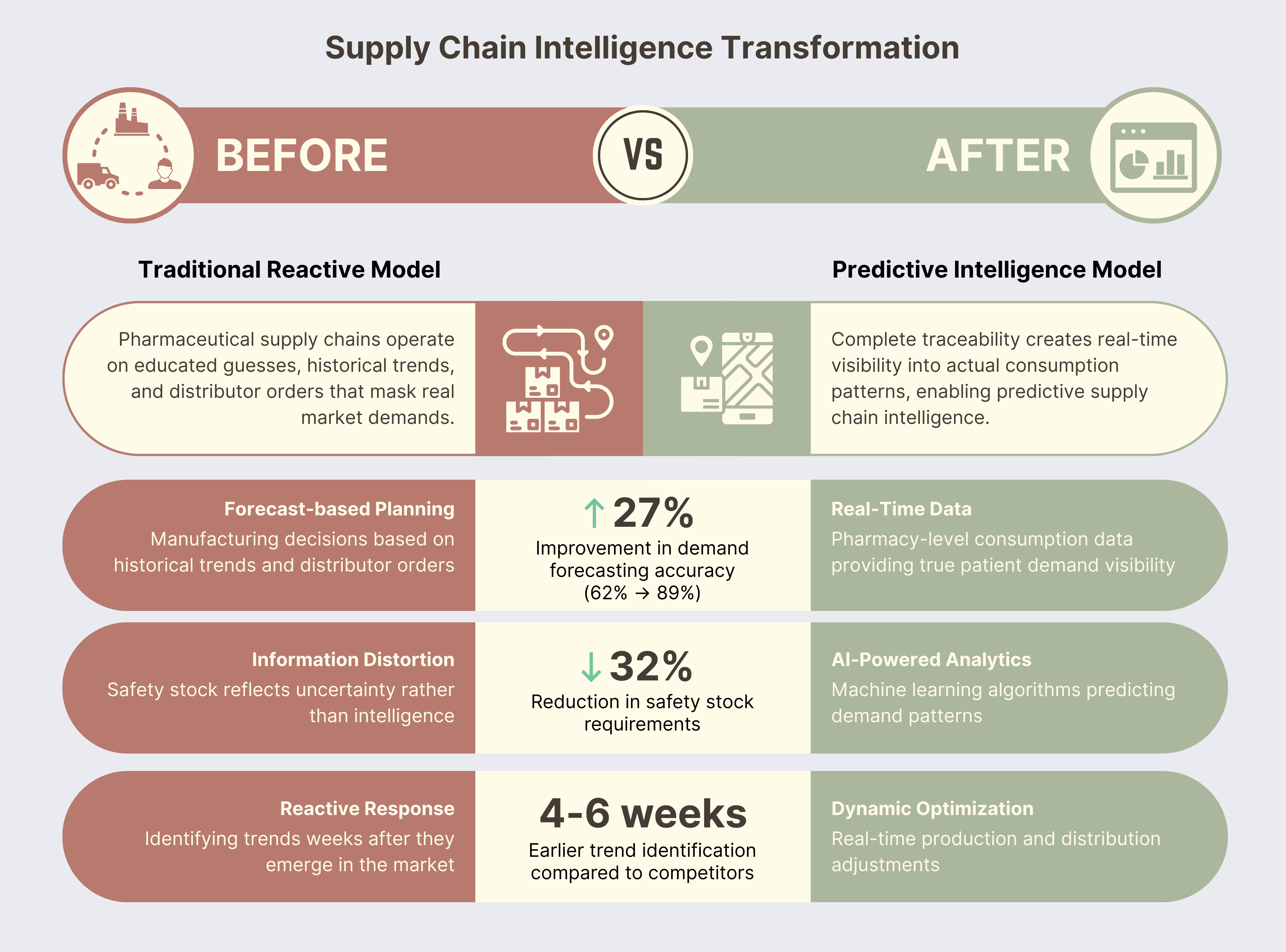
The Traditional Model: Pharmaceutical supply chains operate on educated guesses, historical trends, and distributor orders that often mask real market demand. Companies manufacture based on forecasts, distribute based on orders, and manage inventory with safety stock that reflects uncertainty more than intelligence.
The Transformation: Complete traceability creates real-time visibility into actual consumption patterns, enabling predictive supply chain intelligence that fundamentally changes how companies plan, produce, and distribute products.
Real-World Example: A leading pharmaceutical MNC we worked with discovered that their chronic stockout problems weren't caused by insufficient manufacturing capacity—they were caused by information distortion. Distributors were ordering conservatively due to uncertainty, creating artificial demand signals that led to production planning errors.
With complete traceability providing pharmacy-level secondary sales data and even patient-level consumption insights (tertiary data), they could see real demand patterns for the first time. The transformation was dramatic:
- Demand Forecasting Accuracy: Improved from 62% to 89%
- Safety Stock Requirements: Reduced by 32% while improving service levels
- Working Capital: $3.1 million reduction in inventory investment
- Market Responsiveness: Identified emerging trends 4-6 weeks earlier than competitors
- Real-Time Market Intelligence: Understanding demand patterns as they emerge
- Predictive Analytics: Forecasting trends before they impact supply
- Dynamic Optimization: Adjusting production and distribution in real-time
- Competitive Intelligence: Identifying market opportunities faster than rivals
- Unit-level tracking with real-time data capture
- Advanced analytics platforms with machine learning capabilities
- Integration with ERP, demand planning, and production systems
- Automated alert systems for trend identification
The Traditional Model: Pharmaceutical companies have historically operated on transactional product sales, with little visibility once products left their warehouses. This limited their ability to understand real patient needs, anticipate market shifts, or shape long-term strategic decisions.
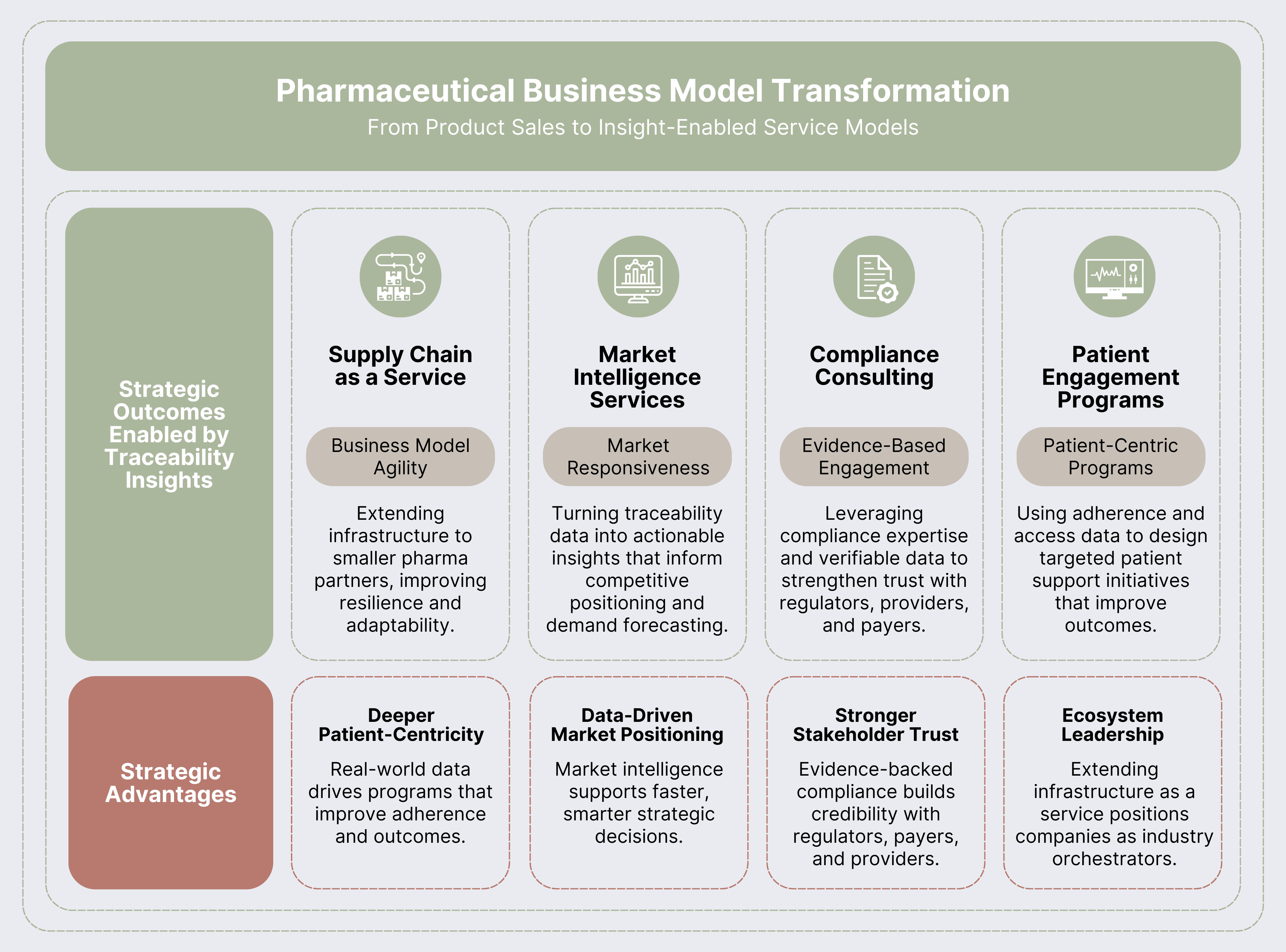
The Transformation: With complete traceability, companies gain real-time visibility into product flow, patient behavior, and market dynamics. This intelligence allows them to evolve from being purely product sellers to orchestrators of service-enabled business models that create deeper value for patients, partners, and regulators.
Real-World Example: A specialty pharmaceutical company initially implemented traceability for European FMD compliance. Within twelve months, they had transformed their approach by using traceability insights to improve patient support and market focus—leading to an 18% uplift in net revenue from optimization.
- Supply Chain as a Service: Robust traceability platforms give pharma firms the agility to adapt business models quickly. Some are even opening up their infrastructure as “Supply Chain as a Service,” helping smaller players achieve compliance and resilience while strengthening their ecosystem role.
- Market Responsiveness: Consumption insights allow dynamic pricing, distribution, and market entry strategies.
- Compliance Consulting: Regulators, providers, and payers increasingly expect transparency. Traceability enables evidence-based engagement by providing verifiable data.
- Patient Engagement Programs: Traceability data reveals where patients struggle with adherence or access. Companies can respond with tailored patient engagement programs that improve outcomes and strengthen provider relationships.
By analyzing secondary and tertiary sales data on consumption patterns and therapy adoption rates, companies can design smarter patient programs and sharpen their commercial focus.
- Deeper Patient-Centricity: Programs informed by real-world data directly improve adherence and patient outcomes.
- Data-Driven Market Positioning: Market intelligence creates foresight into demand shifts and competitive moves.
- Stronger Stakeholder Trust: Evidence-based engagement with regulators, payers, and providers builds credibility.
- Ecosystem Leadership: Extending traceability infrastructure as a service elevates the company’s role within the broader pharmaceutical ecosystem.
- Multi-tenant architecture supporting external clients
- API-enabled integration for partner access
- Advanced analytics and reporting capabilities
- Secure data sharing with role-based access controls
Business Model Innovation Example: One company created a "Pharmaceutical Supply Chain Intelligence Network" where a shared traceability infrastructure standardized data quality and forecasting across partners, reducing stockouts and returns while improving service levels. The program monetized existing capabilities primarily by offsetting cost-to-serve and improving overall network performance.
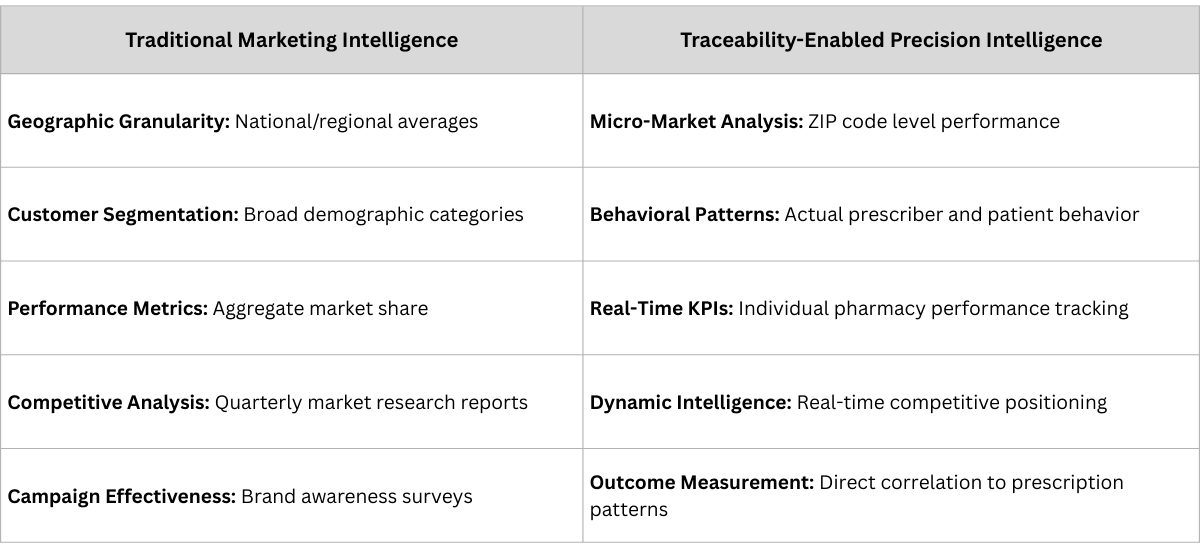
The Traditional Model: Pharmaceutical marketing operates on broad assumptions and aggregated data. Companies launch products nationally, deploy sales forces geographically, and measure success through market share statistics that often obscure more than they reveal about local market dynamics.
The Transformation: Complete traceability generates granular secondary and tertiary sales data that enables precision targeting, micro-market optimization, and data-driven strategic decisions that were previously impossible.
Real-World Example: A pharmaceutical MNC discovered through traceability data, essentially pharmacy-level secondary sales and prescriber-level tertiary data that their diabetes medication was thriving in specific micro-markets invisible in traditional reports.
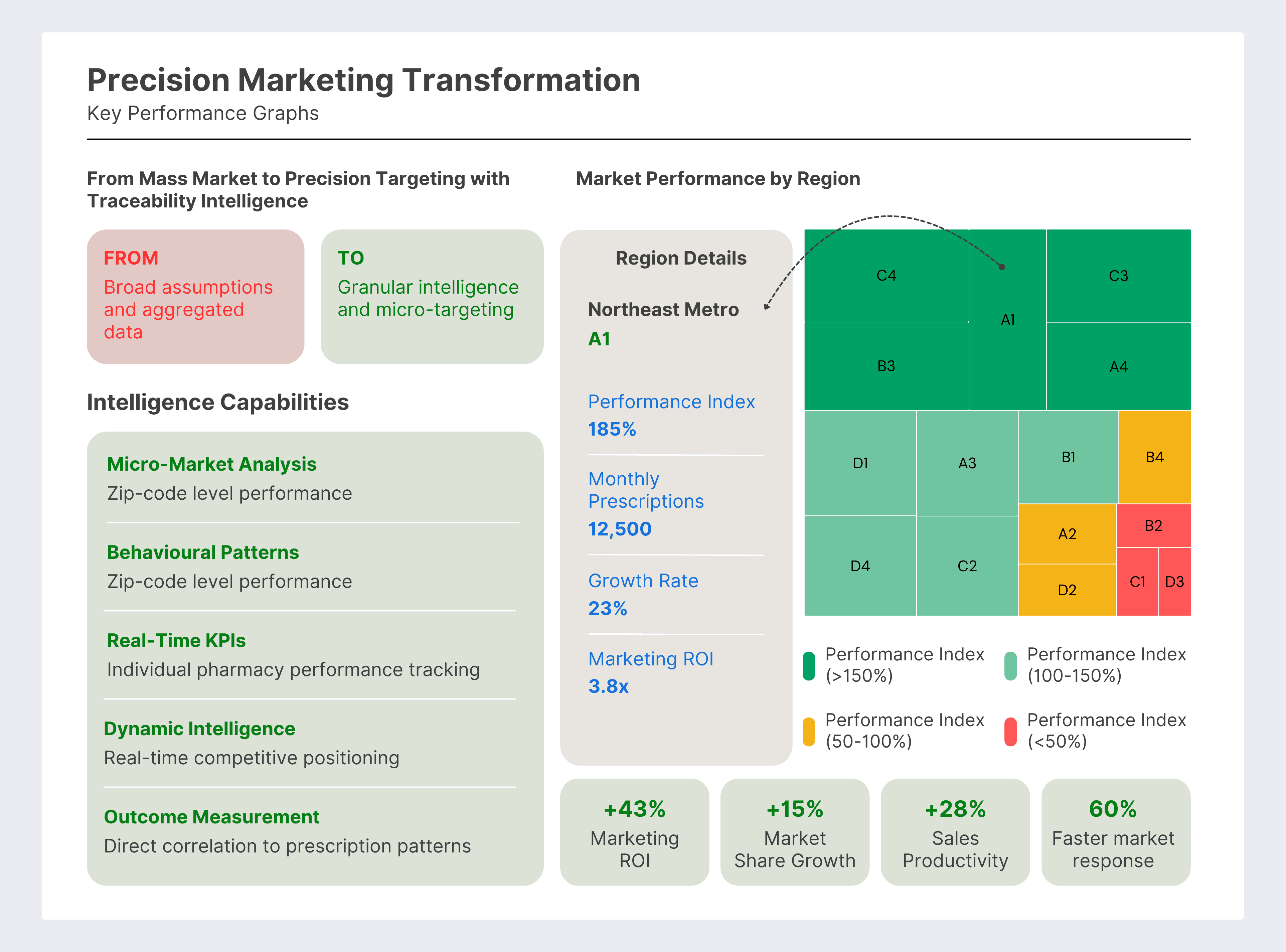
- Marketing ROI: 43% improvement through precision targeting
- Market Share Growth: 15% increase in targeted segments
- Sales Force Productivity: 28% improvement in territory effectiveness
- Strategic Agility: 60% faster response to market changes
- Secondary sales tracking at customer level
- Geographic information systems integration
- Advanced analytics with machine learning
- Real-time dashboard development for field teams
Business Impact: Instead of broad national advertising campaigns, they could identify specific geographic markets where targeted investment would generate the highest returns. Marketing spend became surgical rather than scattered, and results became measurable rather than assumed.
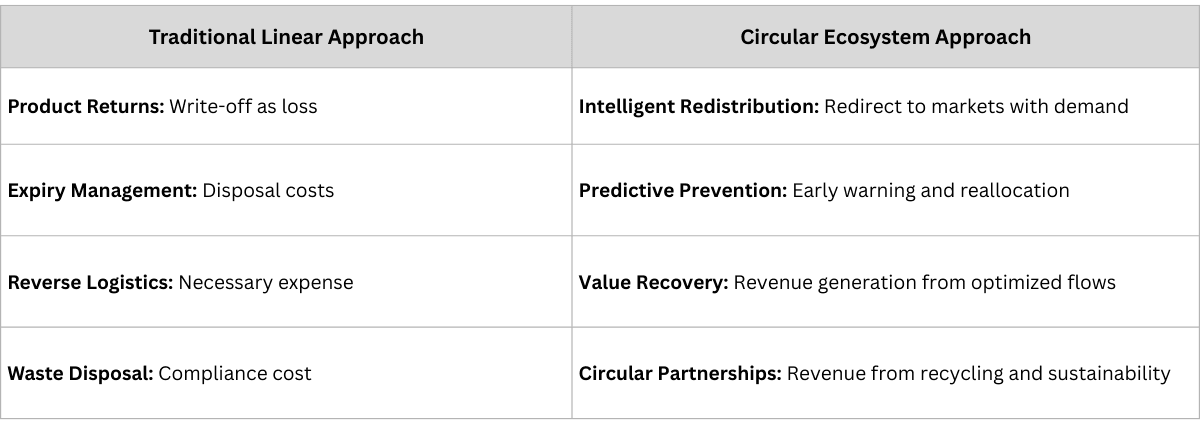
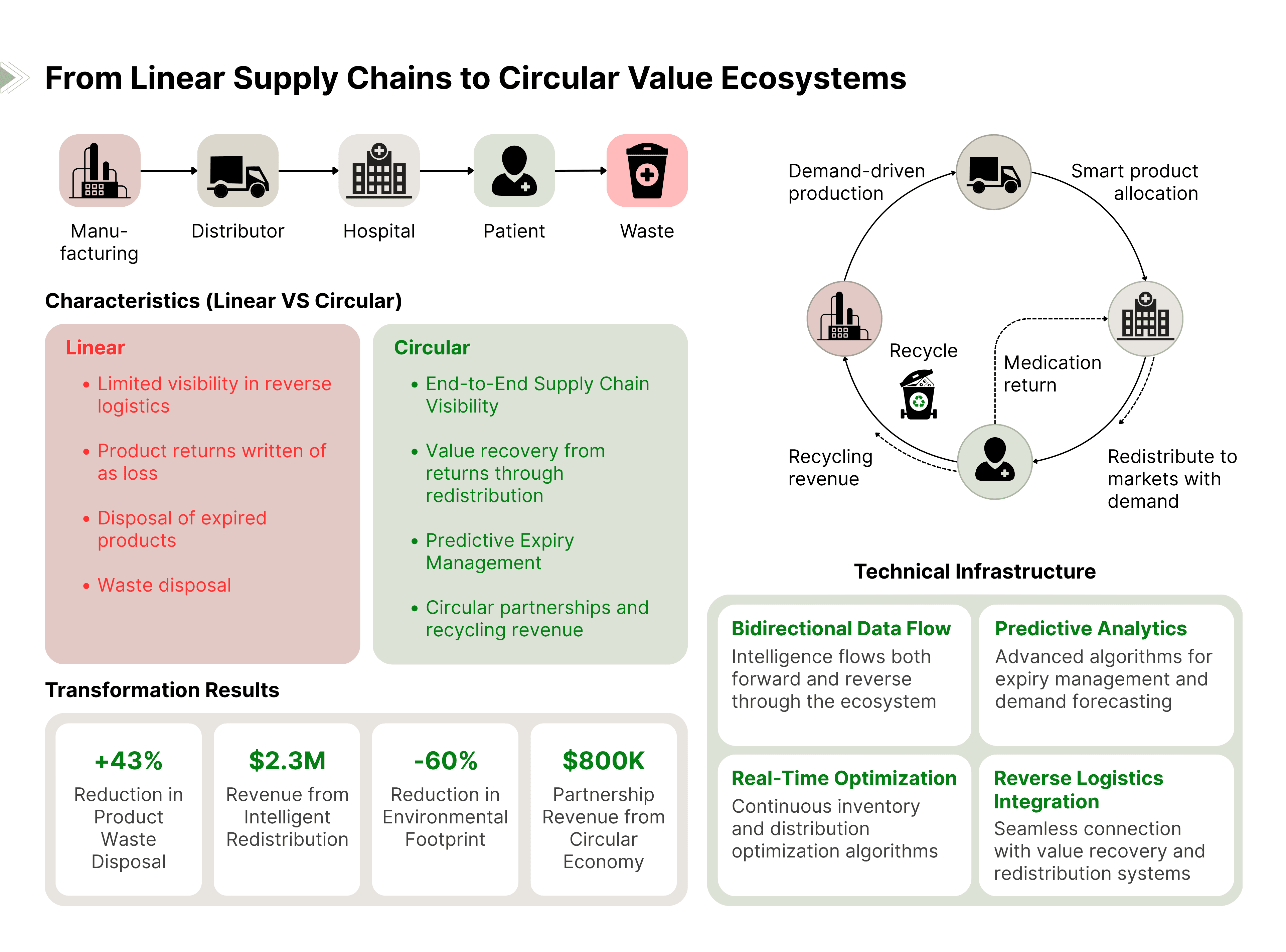
The Traditional Model: Pharmaceutical supply chains are linear processes where products flow from manufacturer to distributor to pharmacy to patient, with limited visibility or intelligence flowing in reverse. Returns, expiries, and disposal are viewed as necessary costs to be minimized but not optimized.
The Transformation: Complete traceability enables the creation of circular value ecosystems where intelligence flows bidirectionally, creating new forms of value at every stage of the product lifecycle.
Real-World Example: A pharmaceutical company transformed their approach to reverse logistics by leveraging traceability data to understand the patterns behind product returns and expiries.

- Waste Reduction: 45% decrease in product disposal
- Recovered Value: $2.3 million via intelligent redistribution
- Sustainability Impact: 60% reduction in environmental footprint
- Partnership Value: $800K equivalent through circular economy initiatives
- Bidirectional data flow capabilities
- Predictive analytics for expiry management
- Real-time inventory optimization algorithms
- Integration with reverse logistics systems
Strategic Innovation: They created partnerships with logistics providers to develop "pharmaceutical value recovery networks" that turn waste streams into revenue streams while improving sustainability metrics.
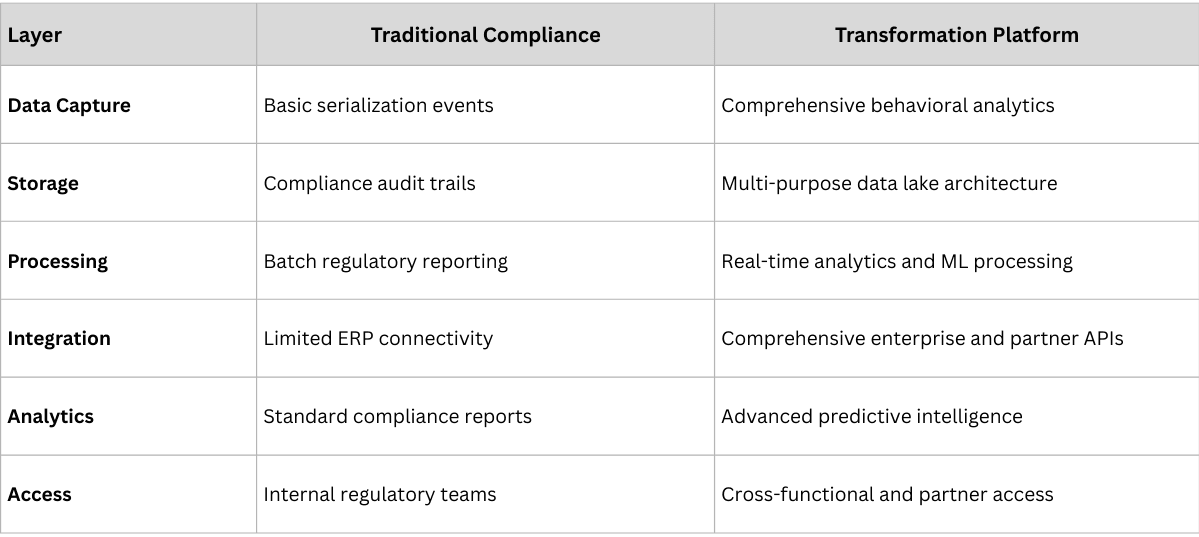
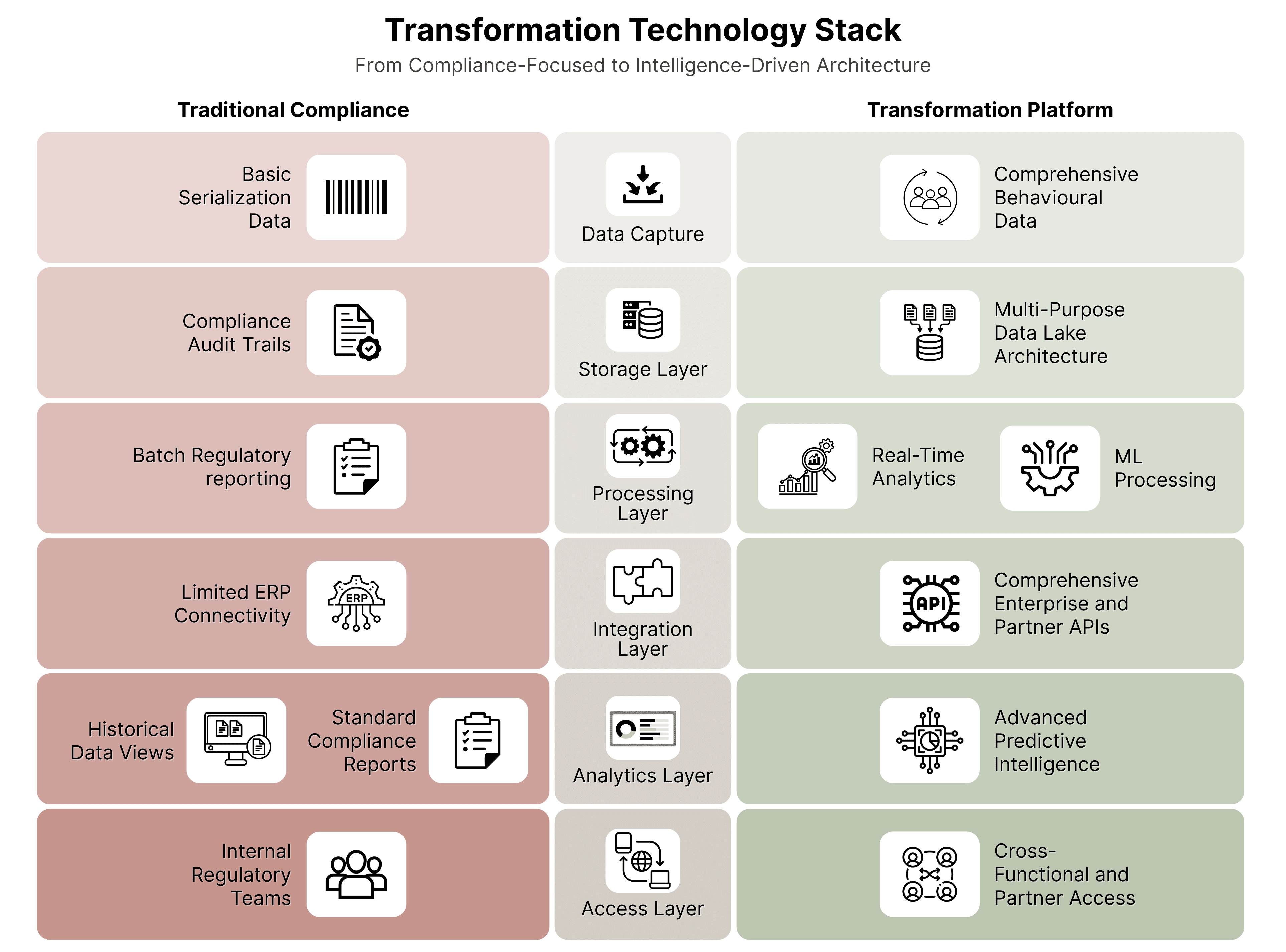
Successful business model transformation requires traceability infrastructure designed for intelligence, not just compliance. The technical architecture decisions made during implementation determine whether traceability becomes a cost center or a competitive advantage platform.
- Capture comprehensive behavioral data, not just compliance events
- Store data in formats optimized for analytics, not just regulatory reporting
- Enable real-time processing for immediate intelligence rather than batch reporting
- Build integration capabilities from day one to support future business model innovation
- Enable partner ecosystem development through secure, scalable API access
- Support multi-tenant architecture for service-based revenue models
- Implement machine learning capabilities for predictive intelligence
- Build real-time processing for immediate operational optimization
- Create visualization layers that democratize data access across the organization
- Design for multi-stakeholder access with appropriate security controls
- Enable data sharing frameworks that support partnership development
- Build scalability for rapid business model expansion
Traditional traceability implementations measure success through compliance metrics—audit results, regulatory violations, and system uptime. Transformation-focused implementations require broader measurement frameworks that capture business impact across multiple dimensions.
- Demand Forecasting Accuracy: Target 80%+ improvement
- Inventory Optimization: 20-40% working capital reduction
- Supply Chain Responsiveness: 50%+ faster trend identification
- Quality Management: 60%+ reduction in recall response time
- Revenue Optimization: % of revenue protected/expanded via adherence, allocation accuracy, and reduced returns
- Margin Improvement: Gross-margin improvement from waste reduction, better mix, and lower cost-to-serve
- Cost Optimization: Supply-chain and reverse-logistics savings realized
- Traceability ROI: Composite of inventory turns, on-time-in-full, shrink/expiry reduction, and forecast accuracy
- Market Intelligence Quality: Ability to capture and use secondary and tertiary sales data for forecasting, targeting, and outcome measurement.
- Competitive Advantage Creation: Measurable differentiation
- Innovation Enablement: New business model development
- Partnership Value: Shared-KPI improvements (service levels, returns, lead-time variance) and mutual cost-to-serve reductions.
Companies that successfully transform their business models through traceability create competitive advantages that compound over time. These advantages become increasingly difficult for competitors to replicate as the gap between leaders and followers widens.
- More data creates better predictions and insights
- Superior analytics attract more partners and customers
- Enhanced intelligence enables better strategic decisions
- More partners increase platform value for all participants
- Service offerings create switching costs for customers
- Ecosystem development generates compounding returns
- Implementation experience accelerates future innovation
- Market intelligence quality improves with scale
- Operational excellence enables competitive pricing
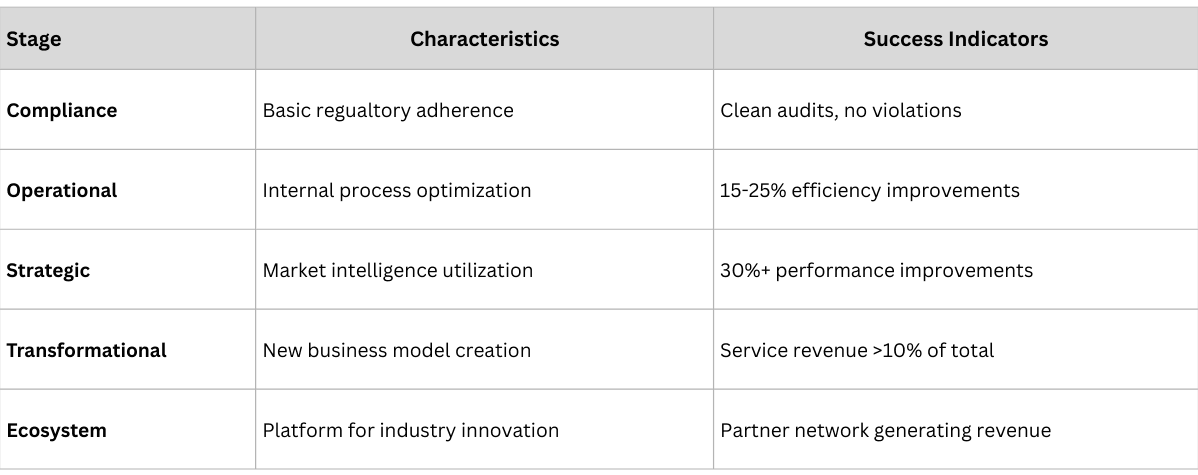
1. Operational Excellence Moat: Companies with superior supply chain intelligence can operate more efficiently, respond faster to market changes, and deliver better customer service than competitors relying on traditional methods.
2. Data and Analytics Moat: Comprehensive traceability data creates insights that competitors cannot replicate without similar infrastructure investments and time to accumulate comparable data sets.
3. Platform and Ecosystem Moat: Service-based business models create customer dependencies and partnership networks that increase switching costs and provide defensive advantages.
4. Innovation and Agility Moat: Real-time market intelligence enables faster strategic pivots, earlier trend identification, and more responsive business model adaptation.
The pharmaceutical traceability transformation is accelerating globally, driven by regulatory requirements, competitive pressures, and technological advancement. Understanding these trends helps companies position themselves for future opportunities.
- Moving beyond compliance to competitive advantage applications
- Focus on insight-driven operating models and ecosystem development
- Advanced analytics and AI integration becoming standard
- Partnership networks creating new industry structures
- Leapfrogging traditional approaches with modern platforms
- Government support accelerating adoption and innovation
- Strong focus on operational efficiency and cost optimization
- Emerging as testing grounds for next-generation capabilities
- High counterfeiting rates creating urgency for transformation
- Infrastructure development enabling modern implementations
- International partnerships driving technology adoption
- Significant potential for circular economy models
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Current implementations use basic analytics. Future developments will include:
- Autonomous supply chain optimization
- Predictive patient adherence modeling
- Real-time fraud detection and prevention
- Automated business model optimization
Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technologies: Moving from pilot projects to production deployments:
- Immutable audit trails for enhanced trust
- Smart contracts for automated transactions
- Cross-industry collaboration platforms
- Decentralized verification networks
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: Environmental monitoring and real-time data capture:
- Cold chain integrity throughout distribution
- Real-time location and condition tracking
- Automated data capture reducing manual processes
- Predictive maintenance for supply chain equipment
Advanced Analytics and Visualization: Real-time business intelligence becoming standard:
- Augmented reality for field team intelligence
- Natural language query interfaces for data access
- Automated insight generation and recommendation systems
- Predictive modeling for strategic planning
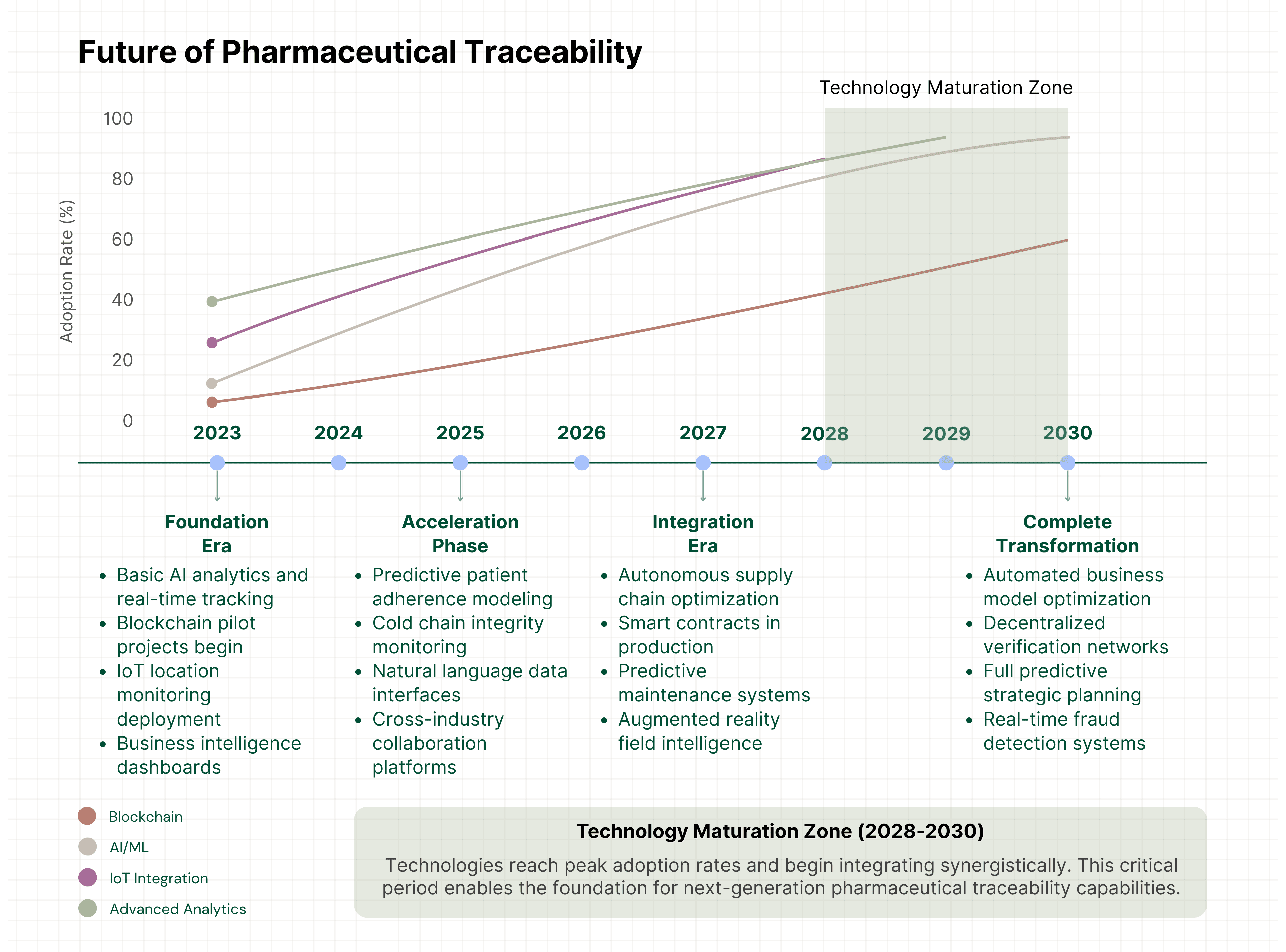
Companies seeking to achieve business model transformation through traceability must approach implementation differently than those pursuing compliance-only objectives. The strategic framework, organizational structure, and success metrics all require transformation-focused design.
- Define transformation objectives beyond compliance
- Identify high-leverage optimization levers and the decisions traceability should improve
- Assess market opportunities and competitive landscape
- Establish transformation success metrics and timeline
- Design technology infrastructure for transformation capabilities
- Build API-first architecture for future ecosystem development
- Implement advanced analytics foundation for business intelligence
- Create data governance framework for multi-purpose utilization
- Deploy core traceability functionality with transformation features
- Build advanced analytics and reporting capabilities
- Develop partner integration and service delivery platforms
- Train teams on transformation opportunities and techniques
- Launch pilot initiatives that apply insights to priority decisions
- Develop partner ecosystem and revenue optimization programs
- Optimize operations based on intelligence and analytics
- Scale successful transformation models across the organization
- Executive sponsorship with transformation mandate
- Operations teams focused on intelligence utilization
- Commercial teams operationalizing insight-enabled plays (micro-market focus, adherence lift, mix optimization)
- Technology teams building platform capabilities
- Communication focused on opportunity, not just compliance
- Training programs for transformation thinking and capabilities
- Performance metrics aligned with business model innovation
- Cultural development supporting continuous transformation
- Over-investing in unproven business models
- Neglecting core compliance requirements during transformation
- Partner ecosystem development challenges
- Technology platform complexity management
- Phased implementation with clear success criteria
- Parallel compliance and transformation development
- Careful partner selection and gradual ecosystem building
- Continuous platform optimization and simplification
Company Profile: Mid-sized specialty pharmaceutical company with strong European presence
- Starting Point: FMD compliance implementation in 2019
- Transformation Vision: Become the "Salesforce of pharmaceutical traceability"
- Business Model Innovation: Platform-as-a-service for smaller pharmaceutical companies
- Service Revenue: $4.2M annually within 24 months
- Customer Base: 47 pharmaceutical companies using platform services
- Market Position: Leading traceability service provider in Europe
- Competitive Advantage: 18-month head start over competitors
- Early recognition of platform potential
- Investment in multi-tenant architecture
- Strong partner ecosystem development
- Focus on customer success and value delivery
Company Profile: Large multinational pharmaceutical corporation with global operations
- Starting Point: DSCSA compliance across US operations
- Transformation Vision: Create "real-time pharmaceutical market intelligence" by unlocking the full value of secondary and tertiary sales data embedded in traceability systems.
- Business Model Innovation: Data-driven precision marketing and strategic planning
- Forecasting Accuracy: 67% improvement in demand prediction
- Marketing ROI: 52% improvement through precision targeting
- Working Capital: $12.3M reduction through inventory optimization
- Market Share: 8% increase in targeted therapeutic areas
- Comprehensive data capture beyond compliance requirements
- Advanced analytics team and capabilities
- Cross-functional transformation approach
- Continuous optimization and learning culture
The transformation of pharmaceutical business models through traceability represents just the beginning of a larger industry evolution. Companies that successfully navigate this transformation will be better positioned for future disruptions and opportunities.
- Core products supplemented by service platforms
- Ecosystem orchestration rather than linear value chains
- Data and intelligence as primary competitive advantages
- Partnership networks as strategic assets
- Revenue tied to patient outcomes rather than product volume
- Real-world evidence generation through traceability data
- Value-based contracts with payers and providers
- Continuous optimization based on performance data
- Sustainable practices as competitive differentiators
- Waste-to-value transformation programs
- Environmental impact optimization
- Circular partnership networks
1. Think Platform, Not Product Design traceability implementations as business platforms capable of supporting multiple use cases and business models rather than single-purpose compliance systems.
2. Invest in Intelligence, Not Just Infrastructure Build advanced analytics capabilities that transform data into actionable intelligence rather than treating traceability as pure operational overhead.
3. Create Ecosystems, Not Just Supply Chains Develop partner networks and service offerings that extend value propositions beyond traditional pharmaceutical boundaries.
4. Measure Transformation, Not Just Compliance Establish success metrics that capture business model innovation and competitive advantage creation rather than focusing solely on regulatory adherence.
The pharmaceutical industry stands at a critical inflection point. Regulatory requirements have made traceability implementation inevitable, but the strategic approach to implementation will determine which companies create lasting competitive advantages and which merely achieve compliance.
The Choice is Clear:
- Follow: Implement traceability for compliance and accept it as a necessary cost
- Lead: Leverage traceability as a platform for business model transformation and competitive advantage creation
The companies making the strategic choice today are already building the capabilities that will define industry leadership tomorrow. They’re protecting and expanding revenue through smarter decisions—optimizing operations, elevating patient outcomes, and building competitive moats that will be difficult for followers to replicate.
Three Key Takeaways for Pharmaceutical Executives:
- Transformation Thinking Required: Approach traceability as business model innovation opportunity, not compliance burden
- Platform Architecture Essential: Build infrastructure capable of supporting multiple use cases and future business model evolution
- Speed Creates Advantage: Early movers build compounding advantages that become increasingly difficult for competitors to overcome
The pharmaceutical traceability transformation has begun. Market leaders are already emerging. The question isn't whether to participate—it's whether to lead or follow.
The companies that recognize traceability as a strategic transformation platform will shape the future of pharmaceutical competition. Those that view it as mere compliance will find themselves at an increasing disadvantage in a market where intelligence, agility, and innovation determine success.
The transformation is happening now. The opportunity window is narrowing. The time for strategic action is today.
The Complete Series:
Next Step: Download our comprehensive white paper "Beyond Track and Trace: How Complete Traceability Transforms Pharma Business Models" for detailed frameworks, case studies, and strategic guidance on implementing traceability for competitive advantage.
About This Series
This transformation analysis draws from extensive experience implementing traceability solutions across pharmaceutical companies ranging from specialty pharma to global multinationals. The business model innovations and strategic frameworks presented have been validated through real-world deployments that have transformed how leading pharmaceutical companies compete and create value.
For strategic discussions about traceability transformation opportunities specific to your organization, contact our team at connect@zelthy.com or send us a DM on LinkedIn.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. "Drug Supply Chain Security Act Pilot Project Program." Program Report, 2023.
- O' Mahony, D., Lynch, A., & McDermott, O. (2024). The Impact of Serialisation on Operational Efficiency and Productivity in Irish Pharmaceutical Sites. Therapeutic innovation & regulatory science, 58(5), 883–896. doi: 10.1007/s43441-024-00662-1
- Cui, Y., Hu, M. and Liu, J. (2023) ‘Value and design of traceability-driven blockchains’, Manufacturing & Service Operations Management, 25(3), pp. 1099–1116. doi:10.1287/msom.2022.116.
- Silva, R.B. and Mattos, C.A. (2019) ‘Critical success factors of a drug traceability system for creating value in a Pharmaceutical Supply Chain (PSC)’, International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(11), p. 1972. doi:10.3390/ijerph16111972.
- Sim, C., Zhang, H. and Chang, M.L. (2022) ‘Improving end-to-end traceability and pharma supply chain resilience with Blockchain’, Blockchain in Healthcare Today, 5. doi:10.30953/bhty.v5.231.
- Kumar, M. (2022) ‘Blockchain technology - A algorithm for drug serialization’, Trends Journal of Sciences Research, 1(1), pp. 61–67. doi:10.31586/ujpp.2022.452.
- Shen, J. et al. (2024) ‘Management of drug supply chain information based on “Artificial intelligence + vendor managed inventory” in China: Perspective based on a case study’, Frontiers in Pharmacology, 15. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1373642.
- Alshemari, A. et al. (2020) ‘Can we create a circular pharmaceutical supply chain (CPSC) to reduce medicines waste?’, Pharmacy, 8(4), p. 221. doi:10.3390/pharmacy8040221.
- Efpia White paper on circular economy (2020) EFPIA.
- Colasse, M. and Leroy, A. (2024) Exploring the Barriers and Drivers of Reverse Logistics Implementation: An Embedded Single Case Study In The Belgian Pharmaceutical Supply Chain. thesis.
- Chaturvedi, A., Gupta, S., Matthews, J., & HFS Research Supply Chain Services. (2023). HFS Horizons Report: Supply Chain Services, 2023. In HFS Horizons Report [Report].
- Juturi, Pawan. (2023). Role of Enterprise Applications for Pharmaceutical Drug Traceability. Universal Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 2. 41-46. doi:10.31586/ujpp.2023.812
- Rajora, N. (2023, August 16). Pharmaceutical drug traceability by blockchain and IoT in enterprise systems. doi:10.31586/ujpp.2023.749
- Zaino, J. (2020, May 21). Case Study: Tracking and Tracing Drugs in the pharmaceutical supply chain. DATAVERSITY.
- Miozza, M., Brunetta, F., & Appio, F. P. (2024). Digital transformation of the Pharmaceutical Industry: A future research agenda for management studies. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 207, 123580. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2024.123580

















